Obesity
Rafael Vazquez
California State University, Los Angeles
Art 3170-01
Professor Aziz
November 2, 2020

- What is Obesity?
Obesity is a complex disease when an individual has an excessive amount of body fat that increases the risk of health problems. It often occurs when a person overeats a lot by intaking more calories consumed, rather than burned by exercise and normal daily living activities. There are reasons why it is difficult for people to not be obese due to lack of exercise and eating malnutrition foods, according to an article on Obesity (Mayo Clinic, 2020).

Research: Facts on Obesity
- How can obesity affect you?
- According to the CDC of obesity, obese people have a higher chance of having severe medical problems (Mayo Clinic, 2020).
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- It can cause heart attacks or other heart problems.
- It can cause swollen feet, ankles and develop lymphodemas in any part of the body,
- Digestive problems
- Sleep apnea (difficulty breathing while sleeping).
- Certain cancers and other major health problems.
- High cholesterol levels

- What are the reasons that can cause obesity?
- According to the CDC for obesity, there are many reasons why many Americans struggle to lose weight or not be obese. Obesity happens from a combination of causes and contributing factors. (Mayo Clinic, 2020).
- 1. Family inheritance. It is not uncommon that obesity can be inherited from people's parents. The reason is that genes can play a role in obesity because your body can affect the amount of body fat you store and where the fat can be distributed in the body. Obesity also has to with that it runs in the family, not just because of the genes people share from their parents/family; it has to do with family members sharing similar eating and activity habits.
- 2. Lifestyle choices.
- Unhealthy diet. Eating foods that contain high-calorie meals, such as sweets, fast food meals, lacking healthier foods (fruits and vegetables), and eating oversized portions. These things can cause weight gain, which may lead to a person becoming overweight or obese - if it occurs often.
- Liquid calories. It is possible to still consume many calories without eating or feeling feel from drinking beverages with high calories. Consuming too many beverages that contain high calories or sugars, such as sodas, juices, or alcoholic beverages, can increase the chances of gaining weight.
- Inactivity. People who live a sedentary lifestyle often have a higher chance of becoming overweight or because. The reason is that they do not exercise or do little no activities, such as daily living activities. It is easier for people with this behavior to consume more calories than burned without doing any exercises or activities to maintain their weight. For example, watching television, going on your smartphone, computer, tablet, or laying down are all sedentary behaviors. All of these things are highly associated with weight gain.
- 3. Social and economic issues. Social and economic problems are linked to obesity. The reason is that there are people in low-income communities that do not have access to healthier foods, have been taught to cook healthier meals, or can only afford to buy foods that non-healthy. It can also be spending time with family and friends, where those influences can lead people to gain weight and have health problems.
- 4. Age. Obesity can occur at any age, whether a person is young or not. As people get older, their muscle mass will begin to decrease, slowing down your metabolism. It makes it difficult to lose weight. Also, by not controlling your eating habits and exercising less as you age, the chances of becoming obese are high.
- 5. Other factors.
- Pregnancies can cause weight gain.
- Stress from work, school, or other problems.
- Lack of sleep, whether is not getting enough sleep or too much sleep can lead to weight gain.
- Previous attempts to lose weight.

- Statistics: Who is more affected by obesity men or women?
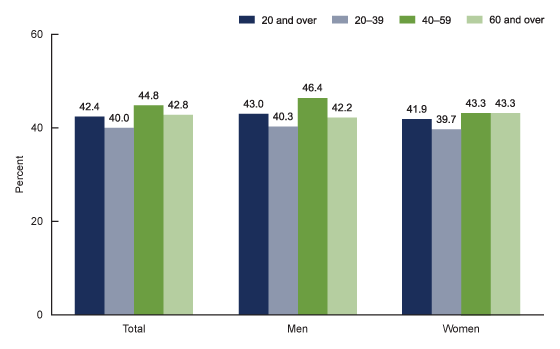
- According to an article about obesity among children and adults, in the years 2017-2018, there were 42.8% of adults in the United States who were obese between men and women.
- Adults aged 40-59 (44.4%) reported higher obesity rates than younger adults ages 20-39 (40.0%).
- Older adults aged 60 and over had obesity rates of 42.8%.
- It is showed that between men and women obesity followed a similar pattern in age.
- Men aged 40-59 (46.4%) had more middle-aged men hat are obese than younger men aged 20-39 (40.3%). Then the data showed 42.2% of males age 60 and above are obese.
- Women aged 40-59 and 60 and above (44.3%) had more middle-aged women that are obese than younger women aged 20-39 (39.7%).
- The results showed that there was no significant difference in the prevalence of obesity between men and women.
Figure 1. Prevalence of obesity among adults aged 20 and over, by sex and age: United States, 2017–2018
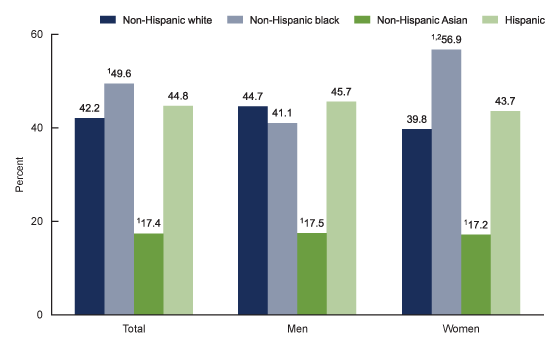
- Statistics: Obesity based on Races
- The graph shows that Non-Hispanic Asian adults reported 17.8%, which is the lowest obesity rate for all races in the years 2017-2018 in the United States.
- In 2017-2018, it was reported that non-Hispanic blacks report the highest percentage (49.6%) of adults in the U.S. that are obese.
- In 2017-2018, Hispanic adults had the second-highest percentage for obesity (44.8%) of adults. Then non-Hispanic Whites had 42.2% of adults in the U.S. that were obese.
- For males, it was reported that the race with the lowest prevalence of obesity was Asians (17.5%), compared to White males (44.7%), and Black males (41.1%). It was reported that Hispanic males that the highest percentage of obese males (45.7%) in the years 2017-2018.
- For females, it was reported that the race with the lowest prevalence of obesity was Asians (17.2%), compared to White females (39.8%), and Hispanic females (43.7%). It was reported that Black females that the highest percentage of obese females (56.9%) in the years 2017-2018.
- Overall, it showed that Black females had a higher prevalence of obesity than Black males.
Figure 2. Age-adjusted prevalence of obesity among adults aged 20 and over, by sex and race and Hispanic origin: United States, 2017–2018
- What can we do to prevent or stop this issue?
- Eat three meals a day without snacking in between, if possible.
- Engage in regular aerobic activity by exercising at moderate (75 minutes) or vigorous (150 minutes) intensity.
- Avoid eating unhealthy foods at night (it is harder to burn calories because you will soon fall asleep).
- Drink plenty of water and avoid sugary beverages.
- Make sure to get plenty of sleep, both children and adults.
- Help the lower-income communities have access to healthier foods at more affordable prices.

Personal Reflection:
- How Obesity Affects Me
The obesity issue affects me because many of my community members and extended family members are obese. Living in a low-income community affects many people. They cannot afford to buy healthy foods, have access to healthier foods at their local grocery stores, and other things. It also affects me because I am Mexican-American, and most of the foods we eat are unhealthy. Earlier in my college years, I was almost obese because I did not take care of myself. Growing up, I was very active and did Cross Country, Swimming, and Track. I ate l whatever I wanted because I would burn off those calories I consumed and felt good about it afterward. However, once I graduated from high school, I no longer participated in sports or physical activities. I quickly began to gain weight after I had graduated from high school. Once I started college, I continued having poor eating habits with little to no physical activities. It affected me because I would stress out a lot about school and had other issues going on at the time. I would eat out a lot and not pay attention to what I was eating. After my first year in college, I had gained a lot of weight and was classified as overweight. It was the first time in my life where I was not in the healthy category. One day I looked in the mirror and realized how big I had gotten and couldn't fit into most of my clothes. I was almost obese and realized that I could have had major health issues at a young age if I continued to gain more weight. However, one day I decided to change that and cut back on sweets, unhealthy foods, sugary drinks, and exercising more. I started feeling better about myself and quickly lost weight and then back to being 'normal.' The reason obesity is important to me is that I have some family members, neighbors, and other people I know who are obese and have health issues. Although we are aware of our bad choices and see ourselves struggling with this, most of us do not change it for the better until it is too late. Losing weight or at least changing your eating habits is easier said than done. However, it does not mean that impossible to overcome this. I also feel that we trap ourselves in a negative mind and say, "I can't do this - it's too hard." It also affects our self-esteem and confidence; the more we do not do anything about it, the worse it will get.
- Why did I choose this issue?
I chose this topic because I see it a lot in my community and have extended family members affected by it. I wanted to know more about why obesity affects many people in low-income communities and the U.S. Also, I wanted to see how much obesity rates have increased over the past few decades in both the city of Los Angeles and the U.S. I believe it is important for people to understand that obesity is a serious health issue, both mentally and physically. People are always on the go and find themselves picking-up fast food meals, junk food, etc. because it is quick and easy rather than make healthier homemade meals. Something needs to be done to help people in low-income communities and other people struggling to help them live healthier lifestyles. It is not only educating people about how eating healthier foods and exercising can help prevent serious health problems - it is about giving them access to healthier foods at affordable prices and encouraging them to get out and some aerobic activities. We need to be aware that obesity is affecting California residents and affecting many people in the U.S. Obesity is a serious problem across the country because many people do not take care of themselves.
References
Biggers, Alana. (2018). How to prevent obesity in kids and adults. Healthline. Retrieved from
https://www.healthline.com/health/how-to-prevent-obesity#prevention-for-adults
Craig M. Hales, M.D., Margeret D. Carroll, M.S.P.H., and Cynthia L. Ogden, Ph.D. (Feburary 2020). Prevalence of obesity and severe obesity among adults: United States, 2017-2018. National Center for Health Statistics. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/databriefs/db360.htm
Mayo, Clinic. (2020). Obesity - symptoms and causes. Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and
causes. Retrieved from
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/obesity/symptoms-causes/syc-20375742
No comments:
Post a Comment